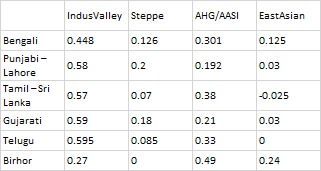
A recent WhatsApp exchange between GL and Sbarr captures a recurring Brown Pundits problem: how genetic data, textual tradition, and social history get collapsed into a single argument and then talk past one another. The immediate trigger was a table circulating online, showing ancestry proportions across South Asian groups; Indus Valley–related, Steppe, AASI, and East Asian components. The numbers vary by region and language group. None support purity. None map cleanly onto caste. That much is uncontroversial. What followed was not a dispute about the data itself, but about what kind of claims the data can bear.
GL’s Position (Summarised)
GL’s argument operates at three levels: historical, linguistic, and genetic.
-
Caste as fluid history
GL argues that the four-fold varna system hardened late. Terms like Vaishya did not always mean “merchant” but originally derived from viś—“the people.” In this reading, Vaishya once referred broadly to non-priestly, non-warrior populations, including farmers and artisans.
-
Elite religion thesis
Early Śramaṇa movements, Buddhists, Jains, Ajivikas, are framed as elite projects. Renunciation, non-violence, and philosophical inquiry required surplus. Most people, GL argues, worshipped local deities and lived outside these doctrinal systems.
-
Genes as complexity, not identity
GL points out that Steppe ancestry and Y-DNA lineages are unevenly distributed. Some peasant groups show higher Steppe ancestry than some Brahmin groups. Maternal lines are largely local. The conclusion is not reclassification, but complication: caste cannot be reverse-engineered from genes. GL’s underlying claim is modest: simple caste narratives do not survive contact with deep history.
Sbarr’s Position (Summarised)
Sbarr’s objections are structural and definitional.
-
Varna as stable social fact
In lived Hindu society, Vaishya has meant merchant since at least the Dharmashastra period. Etymology does not override usage. Peasants were not Vaishyas. Shudras worked the land. Dalits lay outside the system.
-
South Indian specificity
Sbarr stresses that the North Indian varna model does not transplant cleanly into the Tamil world, where Brahmins, non-Brahmin literati, Jain monks, and Buddhist authors all contributed to classical literature. Claims of universal Brahmin authorship are rejected.
-
Genes do not make caste
Even if some peasant or tribal groups show Steppe Y-DNA, this does not make them Brahmins or twice-born. Genetic percentages are low, overlapping, and socially meaningless without institutions.
Sbarr’s core concern is different from GL’s: the danger of dissolving concrete social history into abstract theory.
Where the Debate Breaks Down
The argument falters because the two sides are answering different questions.
-
GL is asking: How did these categories emerge over millennia?
-
Sbarr is asking: How did people actually live, identify, and reproduce hierarchy?
Genes describe populations. Texts describe ideals. Caste describes power. None substitute for the others.
The Takeaway (Without a Verdict)
The ancestry table does not refute caste. The Manusmriti does not explain population genetics. Etymology does not override social practice. What the exchange shows, usefully, is the limit of WhatsApp as a medium for longue-durée history. Complex systems resist compression. When they are forced into slogans, everyone ends up defending a position they did not fully intend. That, more than Steppe percentages or varna theory, is the real lesson here.

Not a bad synopsis.
Maybe a minor quibble or two depending on how the comments play out.
very well summarized. Enjoyed reading it!!
when you correct for region the correlation btwn non-AASI and status is pretty striking and surprising. the exceptions are few; eg jats vs. punjabi brahmins
Hey. Razib,
Could u just put yDNA ballpark numbers for Brahmins vs Autosomal (Steppe / Non Steppe).
Our lankan friend took issue to yDNA data not matching with your post on autosomal (debate escalated due to that very simple thing)
there is more Y in most populations than steppe cuz it seems male-mediated. 2x? sometimes more. but Y is subject to 4x more drift so can fix or disappear too
Depends upon what is being counted in ‘status’ because mixing of ancient systemizing with modern identity politics has rendered the possibility of separation of contemporary status almost impossible.
Search abt.’Backwardness’ to see how both forms of classifications were intentionally jumbled up by colonizers using census as Hindus did not had similar ideas when colonizers demanded them to fill Religion / Caste as colonizers understood it to mean {this is the crux of N Dirks argument}.
Search & check on EPW – How has the Idea of Backwardness Taken Shape in Maharashtra?
Had caste not been made the core mobilizational identity then it was quite possible that one could have diff. religious status {ancient classification} & another modern professional status. Even Ambedkar’s son-in-law is trying to bring forth class politics to forefront & make Dr. Ambedkar a little less great in his new book Iconoclast seeing failure of his political ascriptive hierarchy.
Here are some papers if someone really wants to study what is being referred to as ‘Caste’ in social studies now –
Caste and two types of status. Comparing Dumont and Weber for studies of caste today
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09584935.2023.2169904
———————————————————
Regarding backwardness –
Defining Backwardness Debates in Bombay/Maharashtra
https://t.co/CMQ3B1a4eG
The Pedagogical Account of Parliamentarism at India’s Founding
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/ajps.12768
———————————————————-
Lastly an interesting debate as enlightenment was happening in Europe to highlight the conditions & theories which informed the debates as it was getting set esp. in Indian subcontinent –
Voltaire and Buffon : the controversy on race and “human varieties”. Anthropologies, politics and Enlightenment historiography
https://www.academia.edu/38274105/Voltaire_and_Buffon_the_controversy_on_race_and_human_varieties_Anthropologies_politics_and_Enlightenment_historiography
P.S. –
This view culminated into savage, half-savage etc. global maps. This was the training {though less crude & more ‘Race Science’ crude} Iravati Karve received & yet she challenged it, that’s why i respect her over many others who failed to question / challenge received wisdom in the name of education.
From some comments on Gaurav’s “varNa in Indian history”
Regarding the word Varna (which Gaurav did not want to define.
I (sbarrkum) said it meant color all the way to Indonesia.
outsiders would not be integrated into the varNas but remain outside as a-varNas.
I pointed out a-varna is no color, i.e. Black (physics)
No – it didnt grow because India adopted stupid Socialist methods which dont work before wealth is generated.
Cart before the horse.
Maybe the economy did not grow because 70% of the population (shudras and below) were marginalized
Worse historically Shudras were prevented from learning to read and write by Brahmins.
eg. A Shudra is unfit of receive education. The upper varnas should not impart education or give advice to a Shudra.It is not necessary that the Shudra should know the laws and codes and hence need not be taught. Violators will go to as amrita hell. (Manu IV-78 to 81)
Gaurav seems quite fixated on Brahmins and the Aryans.
In a discussion he says R1a of Brahmin can be high as 50%
Not clear what he means/
Gaurav points to a table from Razib.
(first row in image attached)
Column1: Population
Column2″ N number of samples (51)
Column7: R1a1 Haplogroup (19.61)
Its is pretty simple data. 52 sample of Kashmiri Pandits. Of that 19.61% have R1a1 haplogroup.
However, Gaurav seems fit to interpret this as 19.62% of Brahmins in Kashmir have R1a1 hapologroup.
Impressively misunderstanding a simple data set
As u don’t have basic understanding of plain English and arithmetic (let alone Stats or genomics let me try to make it clear) ;
Remember you posted 25-17 as 7 not 8 when arguing with Saiarav
Take SS for all Brahmin pops from the table – roughly 43% with sample size 367.
Quite foolish strawman to focus on lowest % in the data and post right?
As i told you multiple times; Razib and others have posted data corroborating the fact that roughtly 50% Brahmin yDNA are Steppe related and 50% are IVC and AASI;
If you had basic agency to google and check papers i mentioned you wouldnt be fighting on this hill.
Y chromosome STR variation reveals traditional occupation based population structure in India | bioRxiv
This isnt some controversial claim i was making – As i have been saying just as Razib.
While you seem to have focused on the 50% and missed the point i was trying to make;
50% brahmins are non Steppe – as in share paternal descent with non Brahmins.
The larger point i was making which you seemed to be determined to ignore is that Brahmins and Non brahmins have *Significant* common paternal descent. How deep in the past ? i do not know but roughly 50% or more common
haplogroups – when they separated can shed more light;
This was the point I was trying to make – you went on Tangent focusing on one data point and are calling my responses obsessive.
Maybe the economy did not grow because 70% of the population (shudras and below) were marginalized
So this genius doesn’t understand that the same country saw rapid growth just after economic reforms ; while major Social reforms occurred in 1950s; I don’t think this line of response is Myopic – i was kind earlier – this is Blind. Especially someone who claims to be good with numbers.
Also finally you seem to be happy to club Shudras and Dalits together – thats not true;
While Dalits were indeed marginalized and dehumanised thats not the case for Shudras – no matter what was written in Manusmriti. Even under the Brahmanical Peshwas the 2 Clans which saw maximum power ( theyre practically royalty today whereas descendents of Peshwas are not to found) were from Shudra classes (Holkars and Scindias).
Funny that many of the northern a-varNas are as fair as Savarnas.
Varna does mean color – but it cant be said with certainty that its the reason class-varNa means the same.
But you surely dont have the comprehension to see the nuance.
As u don’t have basic understanding of plain English and arithmetic (let alone Stats or genomics let me try to make it clear) ;
I see that you are Brahmin or Dwija supremacist.
I am tired of reasoning with someone who is ignorant of introductory statistics,
Take SS for all Brahmin pops from the table – roughly 43% with sample size 367.
I have no idea what you mean by SS (Sum of the Squares is the common usage in stats)
Quite foolish strawman to focus on lowest % in the data and post right?
Convenience. First line of your/Razibs data
As i told you multiple times; Razib and others have posted data corroborating the fact that roughtly 50% Brahmin yDNA are Steppe related and 50% are IVC and AASI;
Pretty obvious you cannot form an un-ambiguous sentence that would pass a peer review.
You may read many papers but you dont understand/
Anyway I am done replying.
Maybe Razib might reply, but he has is not know to reply to ignorant questions
Good you are done replying. Even deep down you know you are 100% in the wrong on this one – and hence resorted to name calling. Dont worry i dont want to get into shitstorm – i will keep it civil.
Taken the first right step in the direction of understanding that this isnt the hill to die on. This is a good point for people to come and read how much nonsense an ignorant person can spout before deciding to not reply.