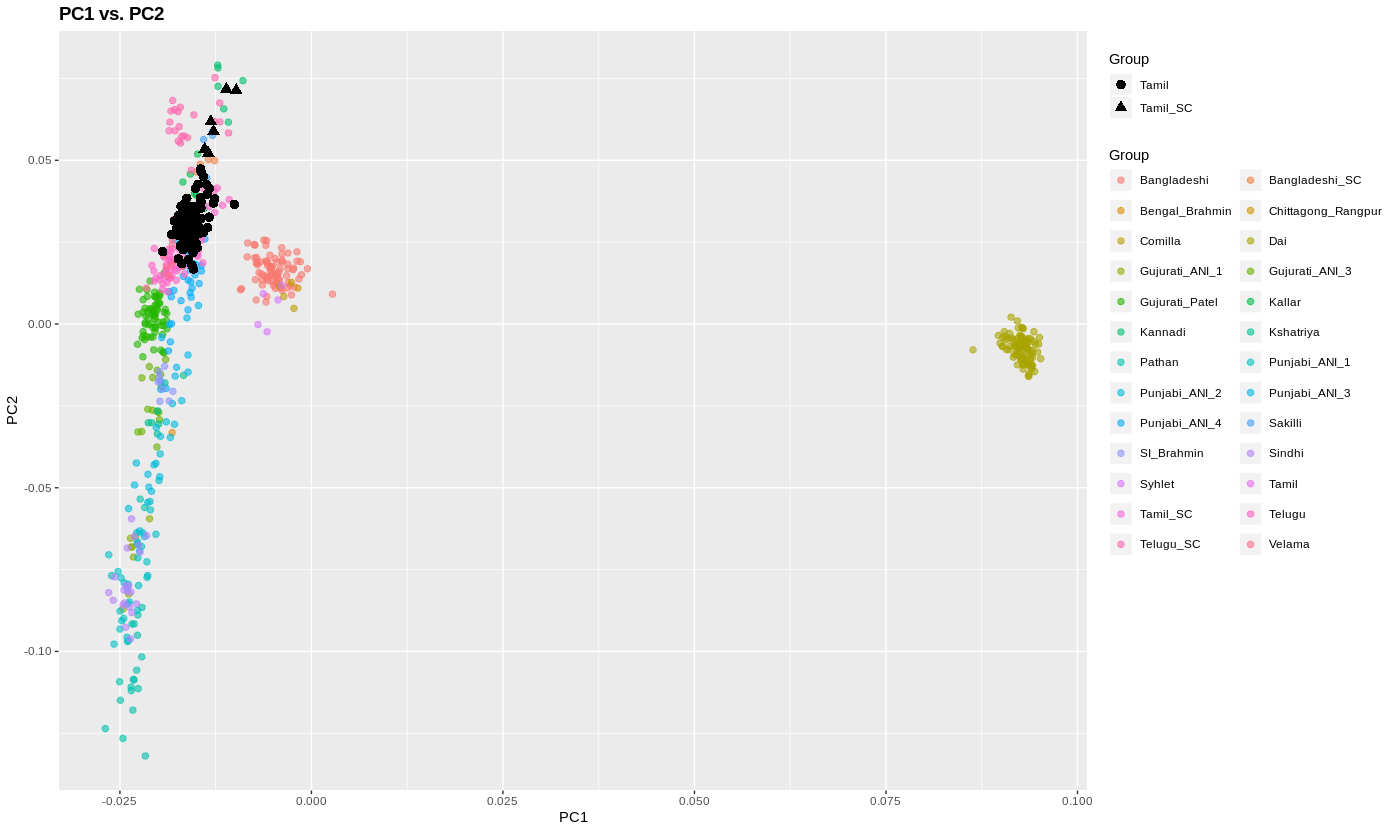
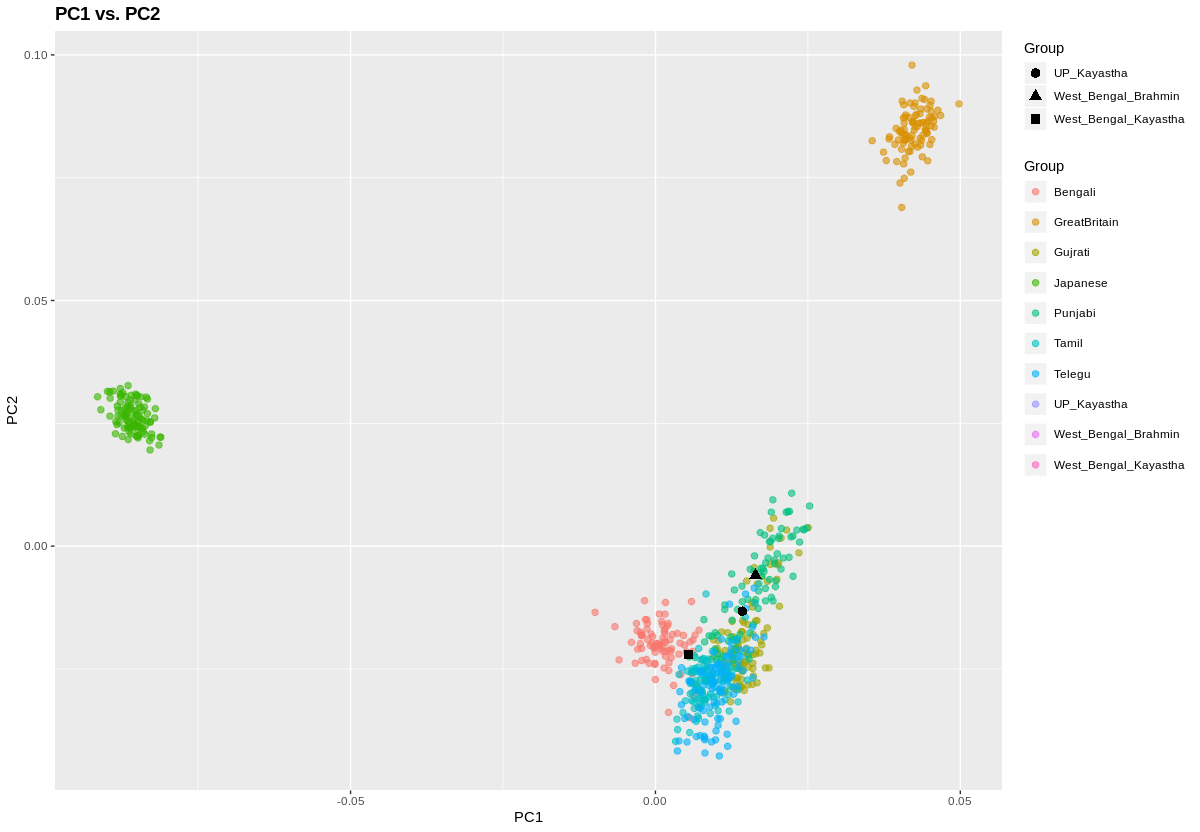
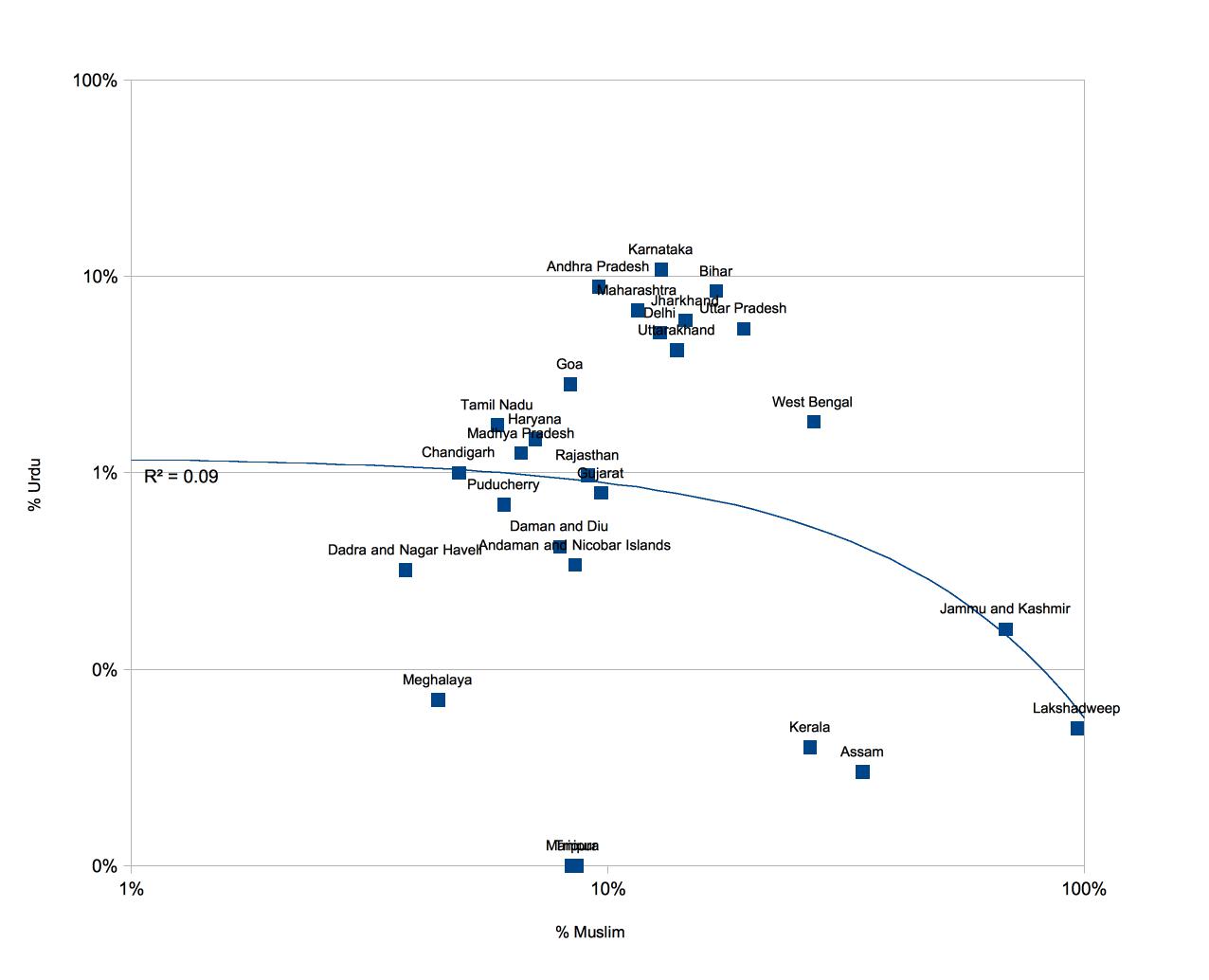
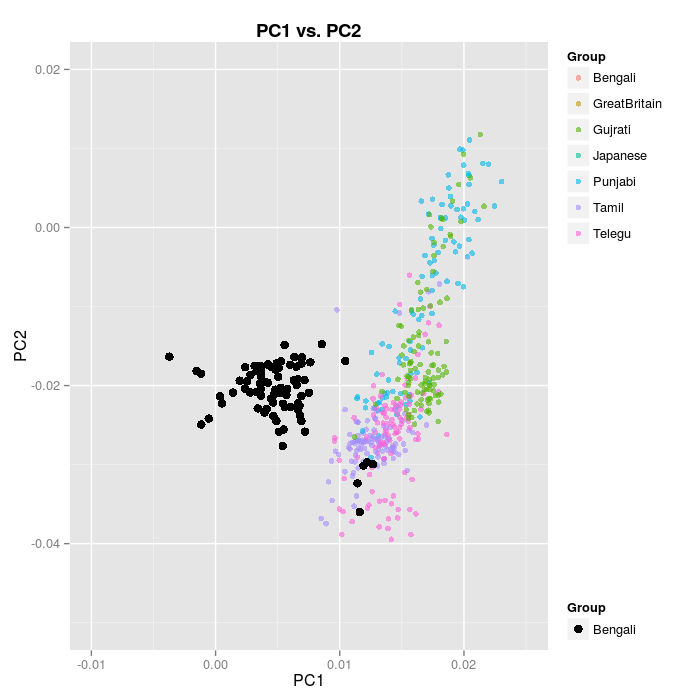
On of the most annoying tropes in modern intellectual discourse, in particular of the postcolonial variety, is its Eurocentrism. That is, the focus on the Western colonial experience is so strong and unwavering that operationally the rest of history becomes prehistory, a formless period which we are ignorant of, when humans were different in fundamental ways.
On of the most annoying tropes in modern intellectual discourse, in particular of the postcolonial variety, is its Eurocentrism. That is, the focus on the Western colonial experience is so strong and unwavering that operationally the rest of history becomes prehistory, a formless period which we are ignorant of, when humans were different in fundamental ways.
Empirically this is of course false. Earlier I have mentioned that the Central Asian Iranian polymath, Al-Biruni, had much to say about India. His was one of the earliest extensive anthropologies we have about the subcontinent from the prespective of an outsider. Though Al-Biruni was from a region which had once had a flourishing Buddhist presence, by the 10th century this had faded from historically memory. Whereas earlier Islamic scholars from previous centuries allude to the persistence of Buddhists in what is today Central Asia and Afghanistan, by Al-Biruni’s lifetime non-Muslims were in sharp retreat (though in the fastness of area like Chitral paganism persisted for a thousand years).
In any case, here are some extracts of Al-Biruni on Indian religion:
The belief of educated and uneducated people differs in every nation; for the former strive to conceive abstract ideas and to define general principles, while the latter do not pass beyond the apprehension of the senses and are content with derived rules, without caring for details, especially in questions of religion and law, regarding which opinions and interests are divided.
With regard to God, the Hindus believe that he is one, eternal, without beginning and end, acting by free will, almighty, all-wise, living, giving life, ruling, and preserving; one who is unique in his sovereignty, beyond all likeness and unlikeness, and neither resembling anything nor having anything resemble him. In order to illustrate this, we shall produce some extracts from the Hindu literature….
…
This is what educated people believe about God. They consider the unity of God as absolute, but that everything beside God which may appear as a unity is really a plurality of things. The existence of God they consider as a real existence, because everything that exists, exists through him. It is not impossible to think
…
If we now pass from the ideas of the educated people among the Hindus to those of the common people, we must first state that they present a great variety. Some of them are simply abominable, but similar errors occur also in other religions. Nay, even in Islam we must decidedly disapprove of the anthropomorphic doctrines, the teachings of the Jabriyya sect, the prohibition of the discussion of religious topics, and such like. Every religious sentence destined for the people at large must be carefully worded, as the following example shows. Some Hindu scholar calls God “a point,” meaning to say thereby that the qualities of bodies do not apply to him. Now some uneducated man reads this and imagines that God is as small as a point, and he does not find out what the word “point” in this sentence was really intended to express. He will not even stop with this offensive comparison, but will describe God as much larger, and will say, “He is twelve fingers long and ten fingers broad.” Further, if an uneducated man hears what we have mentioned, that God comprehends the universe so that nothing is concealed from him, he will at once imagine that this comprehending is effected by means of eyesight; that eyesight is only possible by means of an eye, and that two eyes are better than only one; and in consequence he will describe God as having a thousand eyes, meaning to describe his omniscience.
Similar hideous fictions are sometimes met with among the Hindus, especially among those castes who are not allowed to occupy themselves with science, of whom we shall speak hereafter.
As the word of confession, “There is no god but God, Mohammed is his prophet,” is the shibboleth of Islam, the Trinity that of Christianity, and the institution of the Sabbath that of Judaism, so metempsychosis is the shibboleth of the Hindu religion. Therefore he who does not believe in it does not belong to them, and is not reckoned as one of them. For they hold that the soul, as long as it has not risen to the highest absolute intelligence, does not comprehend the totality of objects at once. Therefore it must explore all particular beings and examine all the possibilities.
The point of this post is not to show that Al-Biruni had a good idea of what “Hinduism” was, though I think if you read it on the whole he isn’t that far removed from how some moderns would characterize it. Rather, it is to show that the distinctiveness of Indian religious thought was noticed long before Europeans arrived to create a specific categorization system which we utilize today. The details of the system might deviate from Al-Biruni, or Adi Shankara, but in its broad outlines it’s describing the same thing.
(since some people are not subtle, the title is not to be taken literally)